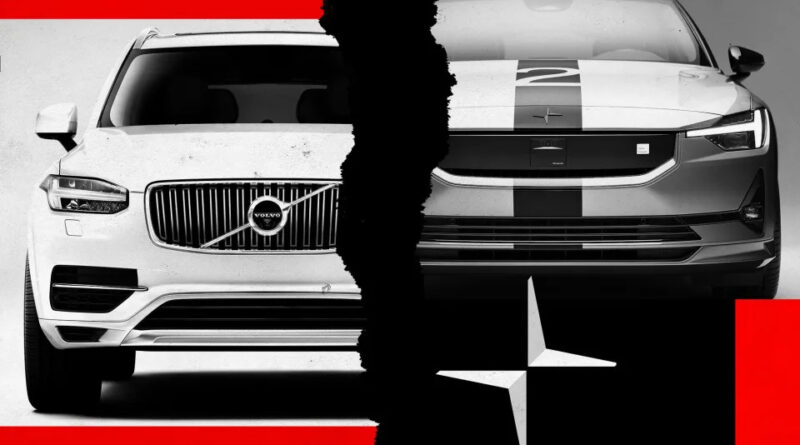
Why Volvo has pulled the plug on its electric car brand
To hear him speak, you would think Volvo Cars’ Scottish chief executive, Jim Rowan, is very much an electric vehicle crusader.
Standing beside the company’s new EX30 as he unveiled the Swedish carmaker’s full-year results on Thursday, Rowan said Volvo was leading “a paradigm shift for us and for our entire industry,” boasting that only Tesla had stronger profit margins on sales of electric cars.
But that enthusiasm apparently no longer extends to Polestar, Volvo’s dedicated electric marque.
On Thursday, Volvo said it would no longer provide financial support to Polestar and would look at offloading some of its 48 percent stake in the company to other shareholders, including China’s Geely. (Most of the rest of Polestar is already owned by Geely chairman Eric Li.)
The news is the latest blow to Polestar, an early mover in electric cars that has struggled to keep up with premium rivals such as Tesla and which remains heavily loss-making despite its cars receiving critical acclaim.
It is also the latest rupture in the electric vehicle industry. Battery-powered cars were once predicted to dominate the vehicle market by the end of this decade, but their sense of inevitability has faded in recent months as sales slow and targets have been pushed back.
Electric vehicle (EV) sales are expected to decline for the first time in seven years in 2024 in Germany, Europe’s biggest car market, and Renault earlier this week scrapped plans to spin off its EV unit, Ampere, blaming a lack of strong interest from investors and a slowdown in sales.
“There is a bigger-picture story here. After a period of growth, interest in EVs isn’t as strong as it once was,” says Peter Wells, the director of the Centre for Automotive Industry Research at Cardiff University. “There is a loss of momentum in the market.”
Sales of electric cars in the UK flatlined last year, and used car prices plummeted, raising questions about their residual value. Globally, sales rose by 31 percent, according to market research firm Rho Motion, but this compared to 60 percent growth the prior year.
Just as driver interest is moderating, competition is heating up. The market has become increasingly cutthroat as low-priced Chinese manufacturers have expanded internationally, sparking price wars in the US and Europe.
Last week, Tesla’s shares fell by 12 percent after the company warned that growth would be “notably lower” in 2024 than shareholders had become accustomed to.
The Polestar name dates back to a Swedish motorsport team in the mid-1990s but was acquired by Volvo in 2015, five years after the Scandinavian car company was sold to Geely.
It originally served as a prototyping station for Volvo concept cars but was spun out as a separate electric car brand in 2017 as a joint venture between Volvo and Geely.
This year was a peak for electric car optimism; it was the year Theresa May introduced the 2035 ban on new petrol and diesel cars (later moved to 2030 by Boris Johnson before Rishi Sunak reversed the move last year).
Its first model, the Polestar 1 sports car, was released two years later, followed by the £45,000 Polestar 2 in 2020.
In 2022, the company went public in New York at a $20bn (£16bn) valuation. It was one of a clutch of electric carmaker IPOs, many of them start-ups that had yet to sell a vehicle. At the time, Polestar’s chief executive, Thomas Ingenlath, distanced the company from those upstarts, predicting profitability within three years.
But so far, there are few signs of that. Profit has remained elusive, with the company losing $730.9 million in the year to the end of September.
The company delayed the release of its next vehicle, the Polestar 3, last year, and while sales continue to climb, growth has slowed down. Last year, the company cut delivery targets from 80,000 cars to 70,000 and then 60,000. It eventually delivered 54,600 vehicles.
Volvo, which continues to own a 48.3 percent stake, has financially supported the company, including with an $800 million loan in 2022.
Other backers have not kept the faith. Shares have fallen by more than 80 percent in the last 18 months, putting the company’s market value below $4 billion.
“Polestar is an expensive car and a new brand; that combination is quite difficult to sustain in a very competitive part of the market,” says Wells. “The European prestige manufacturers want to be in that market. It is largely sustained by corporate buyers, but there is only so much corporate buying that can go on, and the retail market is harder to reach.”
Polestar has also struggled to make up ground on Tesla, the market leader when it comes to high-end EVs. Decades of development have helped Tesla drive down manufacturing costs. Polestar, which produces its cars at Volvo and Geely factories, does not have the same luxury, Wells says.
Meanwhile, Volvo’s in-house electric car business has also faced setbacks. Issues delayed the release of new cars last year, and just 16 percent of its vehicles were electric last year. Volvo remains a way off its 50-PC target for 2025, and meeting that goal will require more investment, meaning the company is no longer willing to fund Polestar.
Rowan only had optimistic words about the electric vehicle brand on Thursday. “It’s a natural evolution that they spread their wings. They go and get their own funding and become a more independent company,” he said, adding that the companies will continue to work on production and that Volvo will remain a major Polestar shareholder.
Despite this assurance and Geely’s insistence that it would “continue to provide full operational and financial support,” Polestar’s shares fell by 14 percent on Thursday, hitting a new low.
Meanwhile, shares in Volvo Cars, which had traded at all-time lows, jumped by 26 percent. Rowan may insist the relationship is simply becoming more arms-length, but investors celebrated what looked like a breakup.
Broaden your horizons with award-winning British journalism. Try The Telegraph free for 3 months with unlimited access to our award-winning website, exclusive app, money-saving offers, and more.
Source : finance.yahoo.com